1976. Number of Ways to Arrive at Destination
Difficulty: Medium
Topics: Dynamic Programming, Graph, Topological Sort, Shortest Path
You are in a city that consists of n intersections numbered from 0 to n - 1 with bi-directional roads between some intersections. The inputs are generated such that you can reach any intersection from any other intersection and that there is at most one road between any two intersections.
You are given an integer n and a 2D integer array roads where roads[i] = [ui, vi, timei] means that there is a road between intersections ui and vi that takes timei minutes to travel. You want to know in how many ways you can travel from intersection 0 to intersection n - 1 in the shortest amount of time.
Return the number of ways you can arrive at your destination in the shortest amount of time. Since the answer may be large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
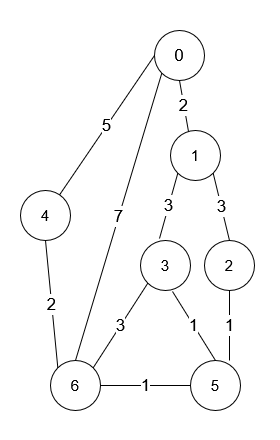
- Input: n = 7, roads = [[0,6,7],[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[6,3,3],[3,5,1],[6,5,1],[2,5,1],[0,4,5],[4,6,2]]
- Output: 4
- Explanation: The shortest amount of time it takes to go from intersection 0 to intersection 6 is 7 minutes.
- The four ways to get there in 7 minutes are:
- 0 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 4 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 2 ➝ 5 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 3 ➝ 5 ➝ 6
Example 2:
- Input: n = 2, roads = [[1,0,10]]
- Output: 1
- Explanation: There is only one way to go from intersection 0 to intersection 1, and it takes 10 minutes.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 200n - 1 <= roads.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2roads[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi <= n - 11 <= timei <= 109ui != vi- There is at most one road connecting any two intersections.
- You can reach any intersection from any other intersection.
Hint:
- First use any shortest path algorithm to get edges where
dist[u] + weight = dist[v], heredist[x]is the shortest distance between node0andx - Using those edges only the graph turns into a dag now we just need to know the number of ways to get from node
0to noden - 1on a dag using dp
Solution:
We need to determine the number of ways to travel from intersection 0 to intersection n-1 in the shortest possible time using bidirectional roads. The solution involves using Dijkstra's algorithm to find the shortest paths and then dynamic programming (DP) to count the number of ways to reach the destination using those shortest paths.
Approach
- Compute Shortest Paths: Use Dijkstra's algorithm to compute the shortest time from intersection 0 to all other intersections. This helps in identifying the shortest paths.
- Construct DAG: Build a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) where edges represent the shortest paths. For each road, check if it contributes to the shortest path in either direction and add the corresponding directed edge to the DAG.
- Topological Sort: Sort nodes based on their shortest distance from 0. This ensures that we process nodes in the order of increasing distance, which is a valid topological order for the DAG.
- Count Paths Using DP: Use dynamic programming to count the number of ways to reach each node from the start node (0) by processing nodes in topological order.
Let's implement this solution in PHP: 1976. Number of Ways to Arrive at Destination
<?php
/**
* @param Integer $n
* @param Integer[][] $roads
* @return Integer
*/
function countPaths($n, $roads) {
...
...
...
/**
* go to ./solution.php
*/
}
// Example Test Cases
$n1 = 7;
$roads1 = [[0,6,7],[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[6,3,3],[3,5,1],[6,5,1],[2,5,1],[0,4,5],[4,6,2]];
echo countPaths($n1, $roads1) . "\n"; // Output: 4
$n2 = 2;
$roads2 = [[1,0,10]];
echo countPaths($n2, $roads2) . "\n"; // Output: 1
?>
Explanation:
- Dijkstra's Algorithm: This algorithm efficiently computes the shortest path from the start node (0) to all other nodes using a priority queue. The shortest paths are stored in the
distarray. - Constructing DAG: For each road, we check if it can be part of a shortest path in either direction. This helps in building the adjacency list for the DAG.
- Topological Sort: Nodes are sorted by their shortest distance from 0 to ensure we process each node after all nodes that can reach it via shorter paths.
- Dynamic Programming: Using the topological order, we count the number of ways to reach each node by summing the ways from all its predecessors in the DAG. This ensures we only consider paths that contribute to the shortest time.
This approach efficiently combines graph traversal and dynamic programming to solve the problem within the constraints.
Contact Links
If you found this series helpful, please consider giving the repository a star on GitHub or sharing the post on your favorite social networks 😍. Your support would mean a lot to me!
If you want more helpful content like this, feel free to follow me:
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar